Pipeline Integrity Assessments
The Wink to Webster Pipeline System’s Integrity Management Program (IMP) utilizes state-of-the-art methods to assess the integrity of the pipeline system.
Hydrostatic pressure tests: Hydrostatic pressure tests, or hydrotests, use pressurized water to identify areas of a pipeline that may need repair. They are generally conducted when a pipeline is being put into service for the first time, being brought back into service after a prolonged period or as part of a periodic integrity assessment.
Prior to a hydrotest, the crude is displaced from the pipeline section and replaced with water in order to minimize potential environmental damage that might result from leaks during the test. The pipeline section is filled with enough water to create significantly more pressure inside the pipeline than is created during normal operations. If the pipeline holds the elevated pressure for a predetermined amount of time, the pipeline is determined to be fit for service. If problem areas are detected, the area is repaired, and the test is repeated until it is completed successfully.
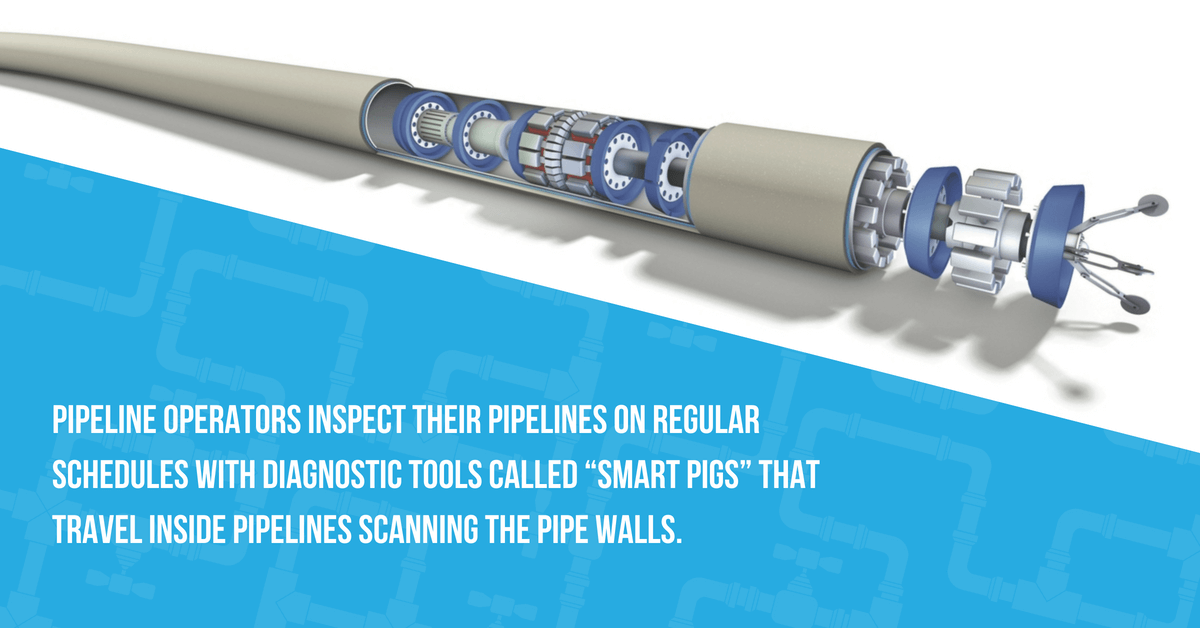
Inline inspection (ILI): Most assessments are performed with inline inspection tools known as “smart pigs.” There are many types of smart pigs, each designed to assess various characteristics of the pipeline and to detect anomalous conditions associated with the pipeline.
Wink to Webster retains qualified, third-party experts who employ proven technologies to conduct their inspections. During an ILI, the third-party experts insert a smart pig that is configured with a combination of sensors to gather data on multiple aspects of the pipeline as it moves through the pipe propelled by the flow of the oil. Use of these inline technologies help us proactively address possible integrity issues in our pipeline system before safety and environmental performance is compromised.
Inline inspections are typically preferable to a hydrotests because they provide more data about the pipeline’s integrity.
Direct assessment: Direct assessments are conducted in cases where it is impractical to conduct a hydrotest or an ILI. This type of test requires excavating the soil from around the pipeline in representative places to directly evaluate the condition of the pipeline.